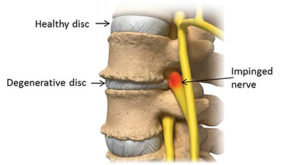
What is degenerative disc disease?
Degenerative disc disease describes the normal progress that occurs to the spine that progresses overtime that leads to pain. Discs are found in the anterior vertebral column that serve to separate the vertebral bodies. These discs function as shock absorbers for the spine.
With time, the discs degenerate leading to decreased flexibility of the spine. Thus, bending and twisting can become a challenge and in turn lead to pain along with a host of other symptoms. The degeneration of discs can result in displacement of disc material than can result in spinal stenosis, spinal cord or nerve root compression.
Risk factors for disc degeneration can be hereditary or occur with age over time as the external matrix of the disc weakens resulting in degeneration. This degeneration can be expedited with injury, strenuous work or sports.
Potential symptoms that you may experience with this condition:
- Back pain
- Muscle spasms
- Pain occurring after certain activities, i.e bending, twisting, sitting, standing or lifting objects
- Pain that maybe constant
- Radiating pain from neck into arms or lower back into legs
- Numbness and tingling in the extremities
- Weakness in the extremities
- Muscle spasms and stiffness
Treatment options for condition:
- Physical therapy:
- Muscle stretching and strengthening,
- Core strengthening.
- Local ultrasound therapy.
- Chiropractor therapy.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Medications:
- Anti-inflammatory therapy,
- muscle relaxants.
- Hot and cold compressors.
- Interventions:
- Diagnostic nerve blocks followed by radiofrequency ablation
- Facet joint injections
- Epidural steroid injections: Interlaminar and Transforaminal
- Spinal cord stimulator
- Trigger point injections.
- Surgery: for severe cases that are refractory to options 1-4 above.
- Developing therapies: Stem cell therapy